What Is Noun Clause : Noun Clauses 1 Proprofs Quiz - Find out why noun clauses that start with a question are used to answer a question.. …what you have learned. this clause is a noun clause. What does noun clause mean? Whatever, whichever, whoever, whomever, how, what, when which, whether, whom, who, why at the beginning. It can be the subject of a sentence, an object, or a complement. How, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why.
A noun clause is a subordinate clause. Like all clauses, a noun clause contains a subject (sometimes represented by one of the words above) and a predicate (a verb and any additional information i want to see what is available before i make a purchase. (what is available is the direct object of the verb see.) at this point, we'll take whatever. Question words like what, how, when etc., can also be used to introduce noun clauses. Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever , and why. Noun clauses generally begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why.
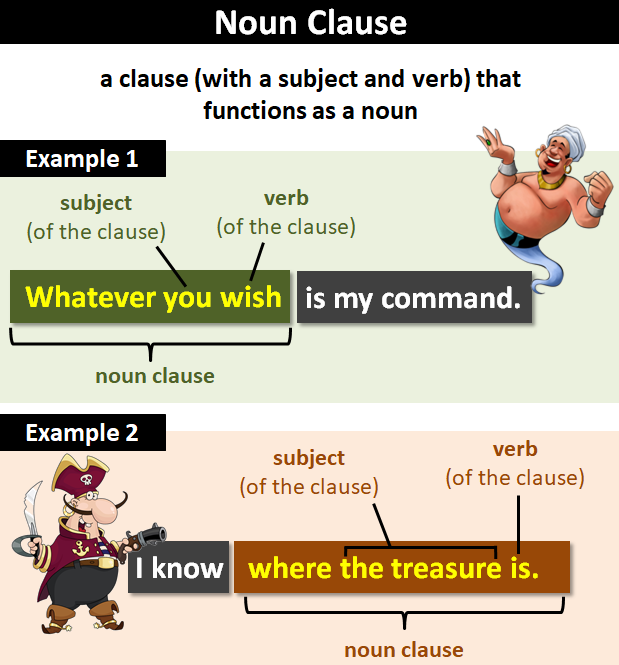
A noun clause is a dependent clause that contains a subject and a verb.
A noun clause is a dependent clause that acts as a noun. As a noun clause does the work of a noun, it can be subject to a sentence, object of a transitive verb, object of a preposition, apposition to a noun, or complement to a linking verb. Just like nouns do, a noun clause names people, things noun clauses have words like; For example (noun clauses shaded) (this noun clause is the direct object of ask.) he knows all about art, but he doesn't know what he likes. (this noun clause is used as. A noun clause serves the same purpose as a noun. It works as a noun in a sentence. What you think does not matter. A noun clause answers the question of what a person is thinking. Like all clauses, a noun clause has a subject and a verb. A noun clause is a subordinate clause. Like all clauses, a noun clause contains a subject (sometimes represented by one of the words above) and a predicate (a verb and any additional information i want to see what is available before i make a purchase. (what is available is the direct object of the verb see.) at this point, we'll take whatever. It can be the subject of a sentence, an object, or a complement.
It works as a noun in a sentence. A noun clause is a subordinate clause in a complex sentence that acts as a noun. You must choose which flavor of ice cream you want. We studied that depend or subordinate clauses are subdivided into three parts: So, what is the noun clause?

Like all clauses, a noun clause has a subject and a verb.
(here the noun clause what she is doing is the object of the preposition in.) noun clauses as compliments. Whatever, whichever, whoever, whomever, how, what, when which, whether, whom, who, why at the beginning. This page has lots of examples of noun clauses and an interactive exercise. Like all clauses, a noun clause contains a subject (sometimes represented by one of the words above) and a predicate (a verb and any additional information i want to see what is available before i make a purchase. (what is available is the direct object of the verb see.) at this point, we'll take whatever. A clause that fulfils the same function as a noun | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples. What i had forgotten was that i had a test today. A noun clause is that contains a finite verb and functioning like a noun within a sentences. A noun clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb; Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever , and why. What is a noun clause? For example (noun clauses shaded) (this noun clause is the direct object of ask.) he knows all about art, but he doesn't know what he likes. Noun clauses are clauses that function as nouns. Let's do a quick review of these two important terms.
What i had forgotten was that i had a test today. Let's do a quick review of these two important terms. A noun clause functions as a noun. The examples below show how they are used noun clauses often use words such as when, what, why, who and other question words, but the speaker may or may not be making a question. Uses and structures of noun clauses along with illustrations.

A noun clause functions as noun in a sentence.
You must choose which flavor of ice cream you want. A noun clause is a subordinate clause. Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever , and why. Like all clauses, a noun clause has a subject and a verb. A noun clause functions as a noun, which means it can be a subject, direct object, indirect object, object of a preposition, predicate nominative, or noun clauses usually begin with words called relative pronouns such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, which, who, whoever, and why. Whatever, whichever, whoever, whomever, how, what, when which, whether, whom, who, why at the beginning. Noun clauses can function as subjects, objects, or complements. Find out why noun clauses that start with a question are used to answer a question. A noun clause is a dependent clause that functions as a noun. Noun clauses are clauses that function as nouns. However, it cannot stand alone as a sentence. So, what is the noun clause? It can be the subject or object of a verb.
